Every filmmaker, screenwriter, or storyteller has wrestled with two words: story and plot. They’re often used interchangeably, even by professionals, but they don’t actually mean the same thing. Yup, a nightmare, isn’t it?
However, it’s crucial that you understand the difference between story and plot, and how they work together, so you can craft compelling films.
At first glance, it might seem like mere semantics. But the distinction shapes how you develop your screenplay, structure your narrative, and ultimately engage your audience. It doesn’t matter if you’re writing an indie drama, a big-budget action flick, or even an animated short, knowing the difference between story and plot can transform your work from good to completely unforgettable.
And that’s where today’s blog comes in. We’ll be breaking down the difference between story and plot, as well as how they work together to create some of cinema’s greatest movies. We’ll even give you some top tips on how to blend story and plot seamlessly into your own work.
Let’s go!

Table of Contents
- Definition of Story
- Definition of Plot
- How Story and Plot Work Together in Film
- Story Structure: The Bridge Between Story and Plot
- Examples of Story vs Plot from Famous Films
- How Celtx Helps Map Story and Plot
- FAQ
- Conclusion
Definition of Story
The story of a film is the ‘what’. It’s the raw material of the narrative including the events, characters, themes, and emotional journeys.
Think of story as everything that could happen in your fictional world, whether or not it makes it into the final cut of your screenplay.
So, what does story include? Well…
- Character, their profiles, plus their desires, fears and relationships.
- Events that occur within the narrative universe (both on and off screen)
- Themes that give the film its deeper meaning
- Chronology of everything that happens, in real world order
“Good story’ means something worth telling that the world wants to hear. Finding this is your lonely task…But the love of a good story, of terrific characters and a world driven by your passion, courage, and creative gifts is still not enough. Your goal must be a good story well told.” – Robert McKee
In short: story is the big picture.
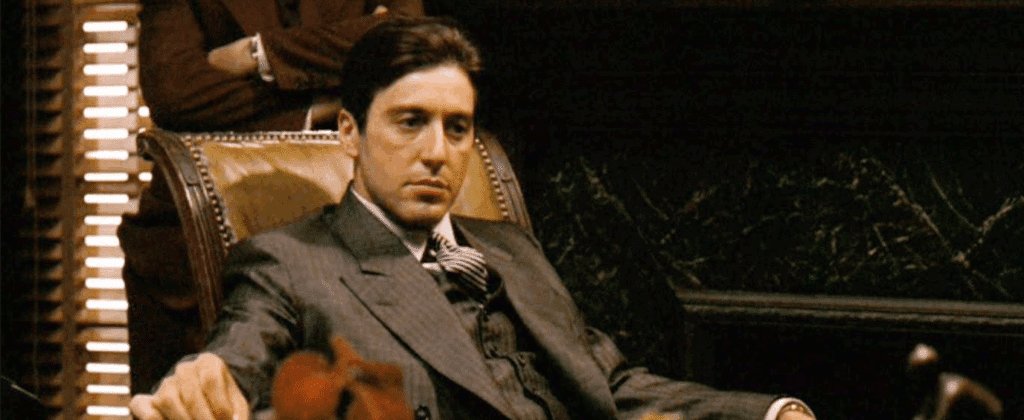
Take The Godfather. The story includes Michael Corleone’s transformation from a reluctant outsider into the ruthless leader of the Corleone family, along with every relevant detail in the family’s saga. That’s the ‘what’.

Definition of Plot
Plot is the ‘how’, the sequence of events as they are presented to thew audience. It’s not just about what happens but how and when it happens on screen.
Plot is also about structure, causality, and emphasis. It’s the deliberate arrangement of story elements to maximise tension, suspense, humor, or emotional payoff.
Key aspects of plot include:
- Order (events don’t have to be shown chronologically, like in Memento or Pulp Fiction)
- Causality (one event leads to another; cause and effect drive momentum)
- Perspective (the storyteller decides what to reveal, conceal, or highlight)
- Pacing (plot controls rhythm including when to slow down and when to speed up)
“A plot point does not have to be a dramatic moment, or major scene, or sequence. A plot point can be a quiet moment for an exciting action sequence. The plot point is whatever you choose it to be … But it is always an incident, episode, or event that is dictated by the needs of the story.” – Syd Field
If we return to The Godfather, we’ll see the plot is the way Francis Gord Coppola chooses to present Michael’s rise to power. The wedding scene introduces the family, the hospital sequence raises the stakes, and the climactic baptism montage contrasts innocence with violence.
It’s the same story but arranged in a way that builds tension and emotional impact as it pans out.

Strong characters and clear structure make your story unforgettable. Use Celtx scriptwriting software to keep your story and plot aligned from draft to draft.
Start Writing Today
How Story and Plot Work Together in Film
Story and plot are two sides of the same coin. You can’t have one without the other. Story is the foundation while plot is the architecture built upon it.
Here’s how they complement each other:
Story Provides Depth; Plot Provides Engagement
A strong story gives characters arcs and meaning. A strong plot makes audiences care in the moment-to-moment of the story.
Story is Timeless; Plot is Experiential
You can summarize the story of Romeo and Juliet in a few sentences. But the plot, the way Shakespeare unfolds it, creates the dramatic irony and heartbreak that make it unforgettable.
Story answers, “what happened?” and the plot answers “why does it matter right now?”
“Plot is people. Human emotions and desires founded on the realities of life.” – Leigh Brackett
Want to dive deeper into the differences between story and plot? Check out this awesome Masterclass lesson from renowned writer Walter Mosley which takes a deep dive!
Story Structure: The Bridge Between Story and Plot
If the story is the what and the plot is the how, then story structure is the framework that organizes both. Structure provides the shape your story and plot take, like the skeleton beneath the skin.
Classic structures such as the three-act structure, the hero’s journey, or five-act dramas give writers a roadmap. These frameworks don’t dictate the details of your story (what happens) or the exact arrangement of your plot structure (how you show it). Instead, they give you milestones including setup, confrontation, climax, and resolution.
For example, in The Lion King, the story is Simba’s journey from cub to king. The plot is how Disney arranges those moments, from Mufasa’s death to Simba’s exile, and ending at his return. The structure is a classic hero’s journey, guiding the timing of those beats we just mentioned.
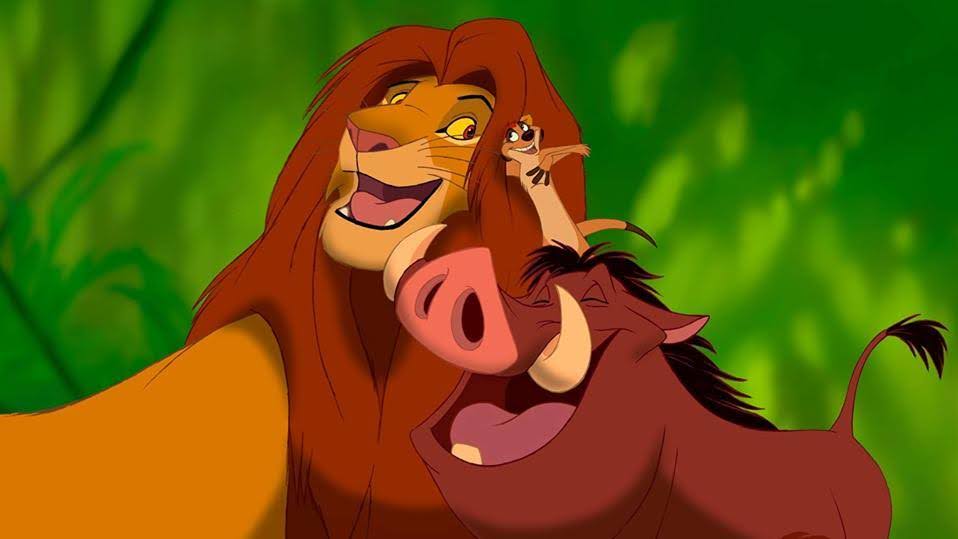

Structure plays a huge role in ensuring your story has meaning, your plot has momentum, and your audience always feels guided, no matter how experimental or straightforward your storytelling is.
For more on writing great story structure, click below:
How to Write a Good Story Using the Five-Act Structure
Three Act Structure in Screenwriting [A Complete Guide]
Examples of Story vs Plot from Famous Films
So now we’ve defined story and plot, let’s take a look at how different filmmakers use them in some of the world’s most popular movies.
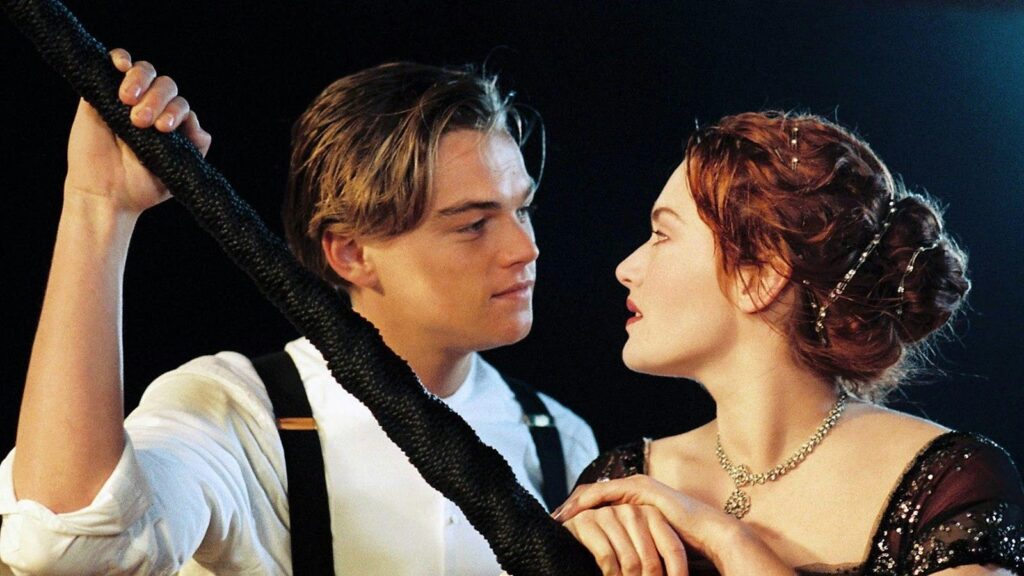
Titanic (1997)
Story
A young aristocrat, Rose, and a working-class artist, Jack, fall in love aboard the doomed RMS Titanic, which ultimately sinks. This leads to Jack’s death and Rose’s survival.
Plot
James Cameron frames the narrative through Rose’s memories as an elderly woman. The film jumps between the present (the treasure hunters) and the past (the doomed voyage), slowly building tension toward the iceberg collision.

Memento (2000)
Story
Leonard suffers from short-term memory loss and is trying to find his wife’s killer.
Plot
Christopher Nolan tells the story backward, disorienting the audience to mirror Leonard’s confusion. The non-linear plot makes viewers experience the same uncertainty as the protagonist.

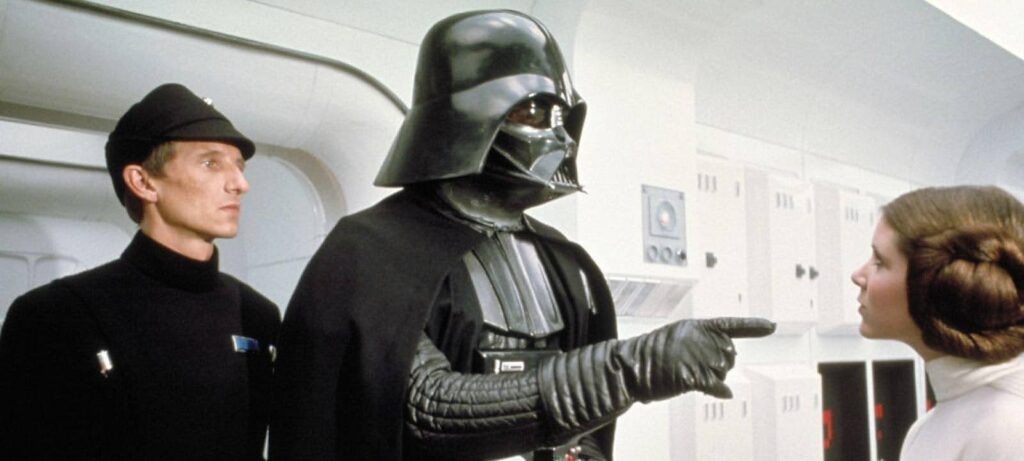
Star Wars: A New Hope (1977)
Story
A farm boy (Luke Skywalker) joins a rebellion, discovers his destiny as a Jedi, and helps defeat the Empire’s superweapon.
Plot
George Lucas structures it as a hero’s journey, carefully pacing revelations and conflicts. From Luke finding Obi-Wan, to the destruction of Alderaan, to the Death Star assault.

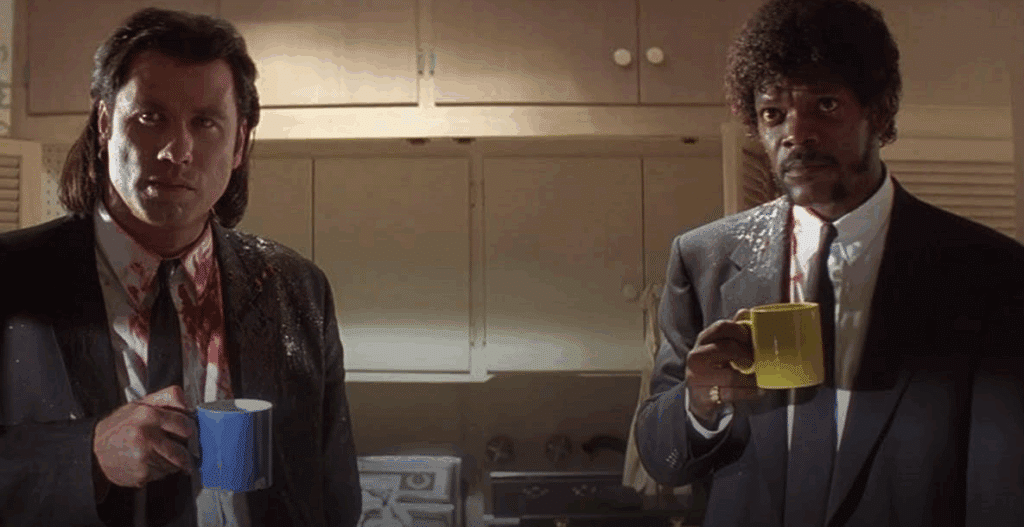
Pulp Fiction (1994)
Story
A series of interconnected events involving hitmen, a boxer, a gangster, and his wife.
Plot
Quentin Tarantino scrambles the chronology, making the story nonlinear. The reordering creates irony, humor, and surprising connections between characters.
In each case, the story is the same regardless of how you summarize it. However, the plot, the chosen arrangement of events, is what gives the film its distinct flavor.

“Plot is no more than footprints left in the snow
after your characters have run by
on their way to incredible destinations.” – Ray Badbury
How Celtx Helps Map Story and Plot
Okay, so understanding story and plot is one thing, but managing them in practice is another. That’s where Celtx comes in!
We offer a powerful pre-production platform that helps writers and filmmakers map out both story and plot that are intuitive and collaborative.
So, how does Celtx support the process?
Story Development Tools
Celtx can help you brainstorm character arcs, relationships, and themes with digital index cards and storyboards. Capture every element of your story world before locking in the plot order.
Check out our storyboarding tools here.
Plot Structuring
Our script editor and beat sheet tools are there to help you arrange events, test different narrative structures, and make sure your pacing flows well. You can easily drag and drop scenes, instantly seeing how changes affect your plot.

Visualization
Storyboards and shot lists allow you to visualize how the story translates to the screen, bridging the gap between raw narrative and cinematic presentation.
Collaboration
Because Celtx is cloud-based, writers, directors, and producers can collaborate in real time. Everyone can stay aligned on both the big-picture story and the moment-to-moment plot.
In other words, Celtx acts as a bridge between your story’s potential and your plot’s execution.
FAQ
Can a film have a strong plot but a weak story?
Yes. A movie might be fast-paced and full of twists but lack emotional depth or thematic resonance. It entertains in the moment but doesn’t stick with audiences.
Can a film have a strong story but a weak plot?
Also, yes. A film may have rich characters and themes but falter in pacing or structure, leaving audiences disengaged despite its potential.
What’s more important, story or plot?
Neither. They’re equally essential. Story provides meaning and plot provides momentum. Great films balance both.
How can beginners practice distinguishing story from plot?
Try summarizing a favorite movie in two ways to sharpen your storytelling instincts. First, writer down everything that happens (story), and then write down the order it’s revealed to you (plot).
Do all films need complex plots?
Not necessarily. Some films, like Boyhood, lean more on story than plot. Others, like Inception, lean heavily on intricate plot mechanics. The right balance depends on your creative goals.
Conclusion
Story and plot are the twin engines that power every great film. Story is the expansive “what”—the characters, events, and themes. Plot is the strategic “how”—the order and structure that keep audiences hooked. Together, they shape the cinematic experience.
By studying how master filmmakers use story and plot differently, and by leveraging tools like Celtx to map both, you can elevate your own screenwriting and filmmaking to the next level.
Ready to bring your own stories to life? Start by mapping out your narrative in Celtx. Whether you’re developing your first short film or your next feature, Celtx gives you the tools to balance story and plot seamlessly.
Start writing with Celtx today and transform your ideas into compelling screenplays.
Up Next:
What is Exposition? (And How to Write it Without Losing Readers)
Exposition sets the stage for your story—introducing characters, world, and context without overwhelming your audience. Learn how to weave exposition seamlessly into your screenplay so it feels natural, not forced.
